Table of Contents
- Biểu Cước Phí Tariff Là Gì? Vai Trò Tariff Trong Xuất Nhập Khẩu
- Donald Trump's tariffs: What's going on and what does it all mean? | US ...
- Fillable Online What is Tariff? Definition of Tariff, Tariff Meaning ...
- Donald Trump's tariffs: What's going on and what does it all mean? | US ...
- How Trump’s Tariffs Could Affect the U.S., Canada and Mexico - The New ...
- What are Trump’s tariff plans and what could they mean for the UK ...
- What are tariffs? What Donald Trump's has said about taxes on imports
- What Is The Meaning of Tariffs? – BMS | Bachelor of Management Studies ...
- How Trump’s Tariffs Could Affect the U.S., Canada and Mexico - The New ...
- What Is a Tariff and How Does It Work? A Guide | CentSai

When it comes to international trade, tariffs are a crucial aspect that can significantly impact the global economy. But what exactly is a tariff, and how does it work? In this article, we'll delve into the world of tariffs, exploring their definition, types, and effects on trade and businesses. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or simply interested in understanding the complexities of global trade, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview of tariffs and their role in shaping the international trade landscape.


What is a Tariff?
A tariff is a tax imposed by a government on imported or exported goods and services. It's a common tool used by countries to regulate international trade, protect domestic industries, and generate revenue. Tariffs can be levied on a wide range of products, from raw materials and manufactured goods to agricultural products and services. The primary purpose of a tariff is to make imported goods more expensive, thereby giving domestic producers a competitive edge in the market.
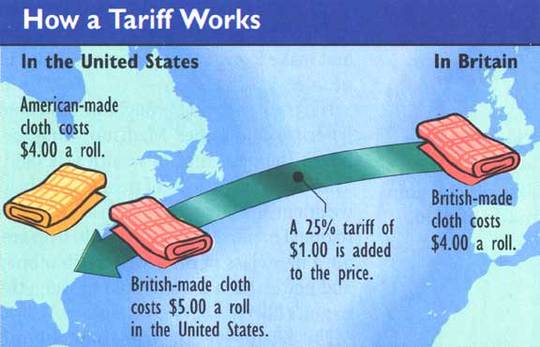

Types of Tariffs

There are several types of tariffs, each serving a specific purpose:

- Ad Valorem Tariff: A percentage-based tariff, where the tax is calculated as a percentage of the imported good's value.
- Specific Tariff: A fixed amount of tax per unit of the imported good.
- Compound Tariff: A combination of ad valorem and specific tariffs.
- Tariff Rate Quota: A two-tiered tariff system, where a lower tariff rate applies to imports within a specified quota, and a higher rate applies to imports exceeding the quota.

How Do Tariffs Work?
The process of imposing and collecting tariffs involves several steps:
- Importation: Goods are imported into a country.
- Customs Declaration: The importer submits a customs declaration, providing details about the goods, including their value, origin, and type.
- Tariff Calculation: The relevant tariff is calculated based on the type and value of the goods.
- Tariff Payment: The importer pays the calculated tariff to the government.
- Release of Goods: The goods are released to the importer after the tariff has been paid.

Effects of Tariffs
Tariffs can have both positive and negative effects on trade and businesses:
- Protection of Domestic Industries: Tariffs can protect domestic industries by making imported goods more expensive, thereby giving local producers a competitive advantage.
- Revenue Generation: Tariffs can generate significant revenue for governments.
- Increased Costs for Consumers: Tariffs can lead to higher prices for consumers, as the cost of the tariff is often passed on to them.
- Trade Wars: Tariffs can lead to trade wars, where countries impose retaliatory tariffs on each other's goods, potentially harming global trade and economic growth.
In conclusion, tariffs are a complex and multifaceted aspect of international trade. Understanding how tariffs work and their effects on trade and businesses is essential for investors, business owners, and individuals interested in the global economy. By grasping the concept of tariffs, you'll be better equipped to navigate the intricacies of international trade and make informed decisions about your investments and business strategies.
For more information on tariffs and their impact on the global economy, visit Fidelity and explore their resources on international trade and investment.
